Seehas
| Seehas (S6) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Overview | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| First service | 29 May 1994 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current operator(s) | SBB GmbH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Former operator(s) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
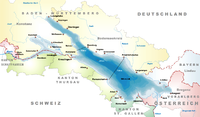
| Termini | Engen Konstanz | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stops | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance travelled | 44 kilometres (27 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average journey time | 50 minutes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Line(s) used | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rolling stock | Stadler FLIRT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seehas is a regional rail service that operates between Engen and Konstanz in the district of Konstanz, in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is managed and operated by SBB GmbH, the German subsidiary of Swiss Federal Railways. It began operation in 1994.
History[edit]
Service began on 23 May 1994, with the extension of existing services from Kreuzlingen (in Switzerland) to Engen. These were operated by Mittelthurgaubahn, a Swiss company.[1] On Mittelthurgaubahn's bankruptcy in 2003–2004, operation passed to EuroTHURBO, the German subsidiary of THURBO. EuroTHURBO itself merged into SBB GmbH in 2005. In 2006, SBB introduced Stadler FLIRT trains on the route and increased the service frequency to every 30 minutes.[2] It operates as part of the Bodensee S-Bahn.[3]
Name[edit]
Seehas literally means "lake hare" in English. The line got its name as a result of a public competition and the subsequent decision by a jury.[4] The name derives from the work Ein Volksbüchlein by Ludwig Aurbacher, written in 1827, in which the Seven Swabians fight a hare. The Seehas is also a traditional mythical animal of the Lake Constance region, which is often depicted as a hybrid of a fish and a hare, for example on Kaiserbrunnen on the market place in Konstanz. In Friedrichshafen there is also the annual festival called Seehasenfest. The Seehas also lends its name to the Seehäsle (lit. 'little lake hare'), a named train that operates between Radolfzell and Stockach.
Operation[edit]
The service uses the Black Forest Railway from Engen to Singen (Hohentwiel), and then the High Rhine Railway to Konstanz. The length of the route is 44 kilometres (27 mi), and an average journey requires 50 minutes.[5][6] The service is summarized as follows:
- S6: Engen – Mühlhausen (bei Engen) – Singen (Hohentwiel) – Radolfzell – Allensbach – Konstanz
References[edit]
- ^ "Seehas-Jubiläum mit Zugtaufe in Singen". Singener Wochenblatt (in German). 9 October 2020. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ "2.500 Tage SBB Deutschland GmbH" (PDF) (in German). SBB GmbH. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ "S-Bahn Bodensee" (in German). Retrieved 9 May 2024.
- ^ "25 Jahre Nahverkehr – der Seehas will sein Angebot weiter verbessern". 15 October 2019. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "SBB GmbH – Unterwegs mit dem seehas" (PDF) (in German). SBB GmbH. 2019. Retrieved 27 February 2021.
- ^ "Fahrplan-Netzkarte 2024 [Railway network and services near Lake Constance 2024]" (PDF) (in German). THURBO. 10 December 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2023.
External links[edit]
 Media related to Seehas at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Seehas at Wikimedia Commons- Official website (in German)