Timeline of national independence
This list includes sovereign states (list) and states with limited recognition that have declared independence from a predecessor state or an occupying power. Various states have never declared independence throughout their formations and hence are not included in the list. The list generally does not include duplicated entries for states declaring independence in several stages, with the exception of those states that have been militarily occupied for a significant length of time. Subnational entities are usually not included in the list unless they were independent countries prior to joining a larger country (e.g. Zanzibar, which joined Tanganyika to form Tanzania). Some of these dates of independence might be disputed. Entries in the "events" table are written in the present tense.
Timeline[edit]
Decolonization of the Europe[edit]
| Country | Date of current form of government | Birth of current form of government | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty | Date of territorial modification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 November 1989 | People's Republic of Bulgaria was replaced by the Republic of Bulgaria | 681 on territories of the Eastern Roman Empire | (Danubian) Bulgaria | 28 October 1944 | |
| 1185 | Second Bulgarian Empire formed | ||||
| 13 July 1878 | Autonomy within Ottoman Empire recognized internationally by the Treaty of Berlin | ||||
| 22 September 1908 | Independence from Ottoman Empire | ||||
| 28 April 1993 | Current Constitution of Andorra entered force | 1278 | Independence from Aragon | 28 August 2001 | |
| 12 November 1918 | Declaration of the Republic of German-Austria | 17 September 1156 | Privilegium Minus: Sovereignty from Duchy of Bavaria as a Duchy of the Holy Roman Empire | 14 December 1921 | |
| 11 August 1804 | Proclamation of the Austrian Empire | ||||
| 27 April 1945 | Restoration of the Republic of Austria | ||||
| 28 November 1996 | Constitutional amendment abolishes the Supreme Soviet and establishes the National Assembly | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | ||
| 27 July 1990 | Declaration of State Sovereignty of the Belarusian Soviet Socialist Republic | 1945 | |||
| 25 August 1991 | Independence recognized by Soviet Union[1] | ||||
| 21 July 1831 | King Leopold I of Belgium swears allegiance to the constitution making the country a constitutional monarchy | 4 October 1830 | Independence was proclaimed by the provisonial government | 28 June 1919 | |
| 1 July 1962 | |||||
| 3 March 1992 | 3 March 1992 | Independence declared from the SFR Yugoslavia | 25 November 1943 | ||
| 29 April 1991 | Socialist People's Republic of Albania was replaced by the Republic of Albania. | 1190 c. | Principality of Arbër was established by archon Progon. | 1945 | |
| 28 November 1912 | Declaration of independence from Ottoman Empire | ||||
| 28 November 1944 | Albanian state re-established after Italian/German occupation | ||||
| 8 October 1991 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia[note 1] | 879 | Duke Branimir was recognized as an independent ruler of the Duchy of Croatia by Pope John VIII. | 10 February 1947 | |
| 925 | Formation of Kingdom of Croatia by King Tomislav | ||||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, creating Czech Republic and Slovakia | October 1918 | Creation of Czechoslovakia | ||
| 5 June 1953 | Constitutional Act of Denmark | 965 | Harald Bluetooth unifies Denmark | 15 June 1920 | |
| 24 February 1918 | Estonian Declaration of Independence, whereby a republic was declared[Europe 1] | 20 August 1991 | Independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 2] | 1 January 1945 | |
| 29 March 1809 | Diet of Porvoo, birth of Finland as an autonomous state entity within Russian Empire | 6 December 1917 | Independence from Russian Empire declared | 26 January 1956 | |
| 3 January 1918 | Independence from Russia recognized by the highest Soviet executive body, VTsIK | ||||
| 4 October 1958 | Establishment of the current semi-presidential system known as the Fifth Republic | 481 then
843 |
First creation with (Clovis), king of the Franks. Then creation of the Kingdom of France (West Francia), Treaty of Verdun | 10 February 1947 | |
| 22 September 1792 | French Republic founded. | 30 July 1980 | |||
| 23 May 1949 | The Basic Law of Germany comes into effect. | 843 then
962 |
Creation of East Francia
East Francia becomes the Holy Roman Empire (with the Kingdom of Germany as a main part of the empire) |
3 October 1990 | |
| 1815 | German Confederation founded | ||||
| 18 January 1871 | German Empire founded | ||||
| 1954 | German Democratic Republic (commonly referred to at the time as East Germany) declared fully sovereign | ||||
| 5 May 1955 | Federal Republic of Germany (commonly referred to at the time as West Germany) declared fully sovereign | ||||
| 15 May 1991 | Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany ends the Four Power occupation. | ||||
| 11 June 1975 | Third Hellenic Republic | 600 BC | Peloponnesian League / Spartan Alliance | 10 February 1947 | |
| 478 BC | Delian League / Athenian Empire | ||||
| 338 BC | League of Corinth / | ||||
| 3 February 1830 | Modern Greece Independence recognized by the London Protocol as Kingdom of Greece. | ||||
| 23 October 1989 | People's Republic of Hungary was replaced by the Republic of Hungary. | 895 | Principality of Hungary formed | 10 February 1947 | |
| 1 January 2012 | The Basic Law of Hungary comes into effect. | 1000 | Formation of the Kingdom of Hungary by Stephen I of Hungary. | ||
| 930 | The Icelandic Commonwealth established and first meeting held of the Althingi (Parliament). | 1 December 1918 | Iceland becomes sovereign and independent from Denmark as the Kingdom of Iceland but retains a personal union with the King of Denmark. | 1 September 1972 | |
| 1 July 1845 | The Althingi resumes meeting after hiatus since 1799. | 17 June 1944 | Kingdom of Iceland becomes a Republic. | ||
| 21 January 1919 | Elected Irish Parliament Dáil Éireann unilaterally declares Ireland's independence from the United Kingdom | 6 December 1922 | Irish Free State secedes from United Kingdom by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty but remains a dominion of the British Empire | 8 December 1922 | |
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster confers legislative independence from the United Kingdom | N/A | |||
| 29 December 1937 | Constitution of Ireland establishes the roles of Taoiseach and President, and replaces the Irish Free State (or Saorstat Eireann in Irish language) with a new state named Ireland (or Éire in Irish language). | 18 April 1949 | Republic of Ireland Act 1948 terminates the functions of the British King in Ireland's diplomatic relations; domestic United Kingdom law purports that Ireland was one of the King's dominions until this date; Irish law does not accept this interpretation. | 2 December 1999 | |
| 2 June 1946 | Italian Republic founded. | 1720 | Sovereignty of the Kingdom of Sardinia, existing since 1324 as part of the Spanish Empire first and subsequently of the Holy Roman Empire. | 1 January 1948 | |
| 17 March 1861 | Italian unification | ||||
| 25 April 1945 | Disestablishment of the German-backed Italian Social Republic, whereby the unity and independence of the Italian state was restored | ||||
| 17 February 2008 | Kosovo Republic founded | 2008 | Kosovan-Serbian War | 2008 | |
| 7 November 1922 | Constitution of Latvia enforced[Europe 1] | 4 May 1990 | Independence (from Soviet Union) reasserted[note 2] | 1944 | |
| 16 March 2003 | The 2003 Liechtenstein constitutional referendum increases the Prince's powers and makes the country a semi-constitutional monarchy | 18 August 1866 | Dissolution of the German Confederation | 23 January 1719 | |
| 11 March 1990 | Act of the Re-Establishment of the State of Lithuania independence (from the Soviet Union) reasserted, end of occupation[note 2][Europe 1] | 16 February 1918 | Independence declared from Germany and Russia | 27 October 1939 and
3 August 1940 | |
| 23 November 1890 | Separates from union with the Kingdom of the Netherlands, becomes Grand Duchy in its own right | 1945 | End of German occupation during World War II | 19 April 1839 | |
| 13 December 1974 | The State of Malta became a republic | 21 September 1964 | Independence from United Kingdom | 20 August 1801 | |
| 27 August 1997 | Constitution of Moldova (1997) | 27 August 1991 | Independence from Soviet Union[1] | 2 August 1940 | |
| 2 September 1990 | |||||
| 17 December 1962 | Amendment to Constitution of Monaco curtails the power of the prince and establishes the modern National Council | 1297 | François Grimaldi captures the fortress atop the Rock of Monaco. | 1848 | |
| 22 October 2007 | Constitution of Montenegro | 3 June 2006 | Declaration of independence from Serbia and Montenegro. | ||
| 24 August 1815 | Adoption of the constitution of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. | 26 July 1581 | Plakkaat van Verlatinghe signed, independence from Spain | 16 March 1839 | |
| 15 December 1954 | Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands signed | 5 May 1945 | Surrender of Nazi forces occupying the Netherlands | 25 November 1975 | |
(until 2019 Republic of Macedonia) |
17 November 1991 | Constitution of North Macedonia | 8 September 1991 | After a referendum, the Socialist Republic of Macedonia declared independence from Yugoslavia[note 1] | 2 August 1944 |
| 1814 | Constitution of Norway | 872 | King Harald I of Norway unifies the Petty kingdoms of Norway. | 27 February 1930 | |
| 1814 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Denmark. | ||||
| 7 June 1905 | Dissolution of the union between Norway and Sweden. | ||||
| 8 May 1945 | German occupying forces surrender. | ||||
| 4 June 1989 | The first partially free Parliament's vote after 45-year-long Soviet domination | 966 | Adoption of Christianity by the first historically documented Polish ruler Mieszko I. | 15 February 1951 | |
| 11 November 1918 | Poland regains its independence. | ||||
| 2 April 1976 | Constitution of Portugal | 5 October 1143 | Formation of Kingdom of Portugal by Treaty of Zamora signing. | 6 June 1801 | |
| 20 December 1999 | |||||
| 20 May 2002 | |||||
| 22 December 1989 | Romanian Revolution of 1989 | 24 January 1859 | Autonomous Principality of Romania founded; becomes kingdom in 1866 and achieved independence 1878 Ottoman Empire | 10 February 1947 | |
| 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | ||||
| 1600 | Constitution of San Marino | 3 September 301 | Independence from Roman Empire | 1463 | |
| 27 April 1992 | Independence from SFR Yugoslavia, forming the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[note 1] | 780 | 8th century-Creation of the Principality of Serbia in the Southeastern Europe. | 17 February 2008 (disputed) | |
| 8 June 2006 | Republic of Serbia declared legal successor to Serbia and Montenegro, ending the process of the dissolution of Yugoslavia. | 13 July 1878 | International recognition by the Treaty of Berlin. | ||
| 1 January 1993 | Dissolution of Czechoslovakia | October 1918 | Creation of Czechoslovakia | ||
| 13 December 1991 | Constitution of Slovenia | 25 June 1991 | Declaration of independence from Yugoslavia[note 1] | 19 February 1945 | |
| 6 December 1978 | Spanish Constitution | 1479 | Dinastical unification of the Crown of Castile and the Crown of Aragon by the Catholic Monarchs. The governments, institutions, and legal traditions of each kingdom remained independent of each other; alien laws (Leyes de extranjeria) determined that the national of one kingdom was a foreigner in the other Crowns/States. | 26 February 1976 | |
| 1707~1716 | De jure by the Nueva Planta decrees | ||||
| 1831 | Dissolution of crowns and kingdoms and creation de jure, of the unified Kingdom of Spain. | ||||
| 1 January 1974 | Instrument of Government | 970 (Or prior) | Eric the Victorious, the first king of Sweden about whom anything definite is known, becomes king. | 29 March 1809 | |
| 6 June 1523 | Gustav Vasa elected King of Sweden and marking a definite secession from the Kalmar Union. | ||||
| 12 November 1848 | Foundation of the federal state after Sonderbund war | 1291 | Traditional founding | 1815 | |
| 7 August 1815 | Restoration of the Ancien Régime (federalism), reverting the changes imposed by Napoleon Bonaparte. | ||||
| 24 August 1991 | Independence of former Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic from Soviet Union declared.[1] | 882 | Formation of the Kievan Rus' | 30 September 2022 (disputed) | |
| 22 January 1918 | Ukraine declares independence as the Ukrainian People's Republic. | ||||
| 8 December 1922 | The Irish Free State seceded from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland by agreement in accordance with the terms of the Anglo-Irish Treaty and the Irish Free State Constitution Act 1922, however Northern Ireland opted to exclude itself from the Irish Free State two days later creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. | 927 | Kingdom of England | 1603 | |
| 843 | Kingdom of Scotland
(Devolved Parliament since 1999) | ||||
| 1057
1165 |
Kingdom of Wales then
(Annexed by England in 1542) (Devolved Assembly since 1999) | ||||
| 1171 then
1542 |
Lordship of Ireland then | ||||
| 1 May 1707 | Kingdom of Great Britain
(United the parliaments of Scotland and England) |
||||
| 1 January 1801 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland | 6 December 1922
then 8 December 1922 | |||
| 12 April 1927 | United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
(Updated to current name) |
2 December 1999 | |||
| 1274 | Birth of current form of government the Papal conclave in 1274 | 7 June 1929 | Ratification of the Lateran Treaty, making the Vatican City a sovereign state | 11 February 1929 |
Decolonization of the Americas[edit]
Decolonization of the Africa[edit]
| Country | Date of acquisition of sovereignty | Acquisition of sovereignty |
|---|---|---|
| 3 July 1962 | French recognition of Algerian referendum on independence held two days earlier | |
| 11 November 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |
| 1 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 30 September 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 5 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |
| 24 September 1973 10 September 1974 (recognised) 5 July 1975[a] |
Independence from Portugal | |
| 1 January 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 13 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 11 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 6 July 1975 | Independence from France declared | |
| 30 June 1960 | Independence from Belgium | |
| 15 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 27 June 1977 | Independence from France | |
| 28 February 1922 | The UK ends its protectorate, granting independence to Egypt | |
| 12 October 1968 | Independence from Spain | |
| 1 June 1936 5 May 1941 19 May 1941 10 February 1947 19 February 1951 15 September 1952 |
Abyssinian campaign Independence from Ethiopia declared | |
| 6 September 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom under the name Swaziland | |
| 5 May 1941 | Abyssinian campaign | |
| 17 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 18 February 1965 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 6 March 1957 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 2 October 1958 | Independence from France | |
| 24 September 1973 10 September 1974 (recognised) 5 July 1975[b] |
Independence from Portugal declared | |
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomous republic within French Community | |
| 7 August 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 12 December 1963 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 4 October 1966 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 26 July 1847 | Independence from American Colonization Society | |
| 24 December 1951 | Independence from UN Trusteeship (British and French administration after Italian governance ends in 1947) | |
| 14 October 1958 | The Malagasy Republic was created as autonomous state within French Community | |
| 26 June 1960 | France recognizes Madagascar's independence | |
| 6 July 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 25 November 1958 | French Sudan gains autonomy | |
| 24 November 1958 4 April 1959 20 June 1960 20 August 1960 22 September 1960 |
Independence from France | |
| 28 November 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 12 March 1968 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 7 April 1956 | Independence from France and Spain | |
| 25 June 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |
| 21 March 1990 | Independence from South African rule | |
| 4 December 1958 | Autonomy within French Community | |
| 23 July 1900 13 October 1922 13 October 1946 26 July 1958 20 May 1957 25 February 1959 25 August 1958 3 August 1960 8 November 1960 10 November 1960 |
Independence from France | |
| 1 October 1960 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 1 July 1962 | Independence from Belgium | |
| 12 July 1975 | Independence from Portugal | |
| 25 November 1957 24 November 1958 4 April 1959 4 April 1960 20 August 1960 20 June 1960 22 September 1960 18 February 1965 30 September 1989 |
Independence from France | |
| 29 June 1976 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 27 April 1961 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 20 July 1887 26 May 1925 1 June 1936 3 August 1940 19 August 1940 8 April 1941 25 February 1941 10 February 1947 1 April 1950 26 June 1960 1 July 1960 |
Union of Trust Territory of Somalia (former Italian Somaliland) and State of Somaliland (formerly British Somaliland) | |
| 11 December 1931 | Statute of Westminster, which establishes a status of legislative equality between the self-governing dominion of the Union of South Africa and the UK | |
| 31 May 1910 | Creation of the autonomous Union of South Africa from the previously separate colonies of the Cape, Natal, Transvaal and Orange River | |
| 9 July 2011 | Independence from Sudan after a civil war. | |
| 1 January 1956 | Independence from Egyptian and British joint rule | |
| 9 December 1961 | Independence of Tanganyika from the United Kingdom | |
| 30 August 1958 | Autonomy within French Union | |
| 27 April 1960 | Independence from France | |
| 20 March 1956 | Independence from France | |
| 1 March 1962 | Self-government granted | |
| 9 October 1962 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 24 October 1964 | Independence from the United Kingdom | |
| 11 November 1965 | Unilateral declaration of independence by Southern Rhodesia | |
| 18 April 1980 | Recognized independence from the United Kingdom as Zimbabwe |
Decolonisation of Oceania[edit]
Decolonisation of Asia[edit]
Country comparison[edit]
The 15 states may be divided into four subregions. Not included in these categories are the several de facto independent states presently lacking international recognition (read below: Separatist conflicts).
| Subregion | Country | Symbols | Independence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flag | |||
| Central Asia | Kazakhstan
(Republic of Kazakhstan) |
16 December 1991 | |
| Kyrgyzstan
(Kyrgyz Republic) |
31 August 1991 | ||
| Tajikistan
(Republic of Tajikistan) |
9 September 1991 | ||
| Turkmenistan
(formerly the Republic of Turkmenistan) |

|
27 October 1991 | |
| Uzbekistan
(Republic of Uzbekistan) |
1 September 1991 | ||
| Total Central Asia | |||
| Eastern Europe | Belarus
(Republic of Belarus) |
25 August 1991 | |
| Moldova
(Republic of Moldova) |
27 August 1991 | ||
| Russia
(Russian Federation) |

|
12 December 1991 | |
| Ukraine | 
|
24 August 1991 | |
| Total Eastern Europe | |||
| Baltics | Estonia
(Republic of Estonia) |
20 August 1991 | |
| Latvia
(Republic of Latvia) |
21 August 1991 | ||
| Lithuania
(Republic of Lithuania) |
11 March 1990 | ||
| Total Baltic states | |||
| South Caucasus | Armenia
(Republic of Armenia) |
23 September 1991 | |
| Azerbaijan
(Republic of Azerbaijan) |
18 October 1991 | ||
| Georgia
(formerly the Republic of Georgia) |

|
9 April 1991 | |
| Total South Caucasus | |||
Timeline of national independence[edit]
| Country | Continent | Acquisition
of sovereignty |
Date of last
subordination |
Previous governing power |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | July 1747 (Durrani Empire) | 1796 | ||
| Europe | 28 Nov 1912 | Nov 1944[12] | ||
| Africa | 3 July 1962[13] | 3 July 1962[14] | ||
| Europe | 7 Sep 1278[15][16] | Nov 1944[17] | ||
| Africa | 11 Nov 1975[18] | 11 Nov 1975 | ||
| The Americas | 1 Nov 1981[19] | 1 Nov 1981 | ||
| The Americas | 25 May 1810 | 9 July 1816[20] | ||
| Asia/Europe | 28 May 1918 | 23 Sep 1991[21] | ||
| Australia | 9 Oct 1942 [note 28] | 9 Oct 1942 | ||
| Europe | 1156 | 27 Apr 1945[note 29] | World War II Allies | |
| Asia/Europe | 28 May 1918 | 30 Aug 1991 | ||
| The Americas | 10 July 1973[22] | 10 July 1973 | ||
| Asia | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | ||
| Asia | 16 Dec 1971 | 16 Dec 1971 | ||
| The Americas | 30 Nov 1966 | 30 Nov 1966 | ||
| Europe | 25 Aug 1991[note 30] | 25 Aug 1991 | ||
| Europe | 4 Oct 1830 | 1945 | ||
| The Americas | 21 Sep 1981[23] | 21 Sep 1981 | ||
| Africa | 1 Aug 1960 | 1 Aug 1960 | ||
| Asia | 1634 | 1634 | (none) | |
| The Americas | 6 Aug 1825 | 6 Aug 1825 | ||
| Europe | 3 Mar 1992 | 3 Mar 1992 | ||
| Africa | 30 Sep 1966[24] | 30 Sep 1966 | ||
| The Americas | 7 Sep 1822[25] | 29 Aug 1825 (Treaty of Rio de Janeiro) | ||
| Asia | 1 Jan 1984 | 1 Jan 1984 | ||
| Europe | 5 Oct 1908[26] | 5 Oct 1908 | ||
| Africa | 5 Aug 1960[27] | 5 Aug 1960 | ||
| Africa | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | ||
| Asia | 9 Nov 1953 | 9 Nov 1953[28] | ||
| Africa | 1 Jan 1960 | 1 Oct 1961 | ||
| The Americas | 11 Dec 1931 [note 31] | 11 Dec 1931 | ||
| Africa | 5 July 1975 | 5 July 1975[29] | ||
| Africa | 13 Aug 1960 | 13 Aug 1960 | ||
| Africa | 11 Aug 1960 | 11 Aug 1960 | ||
| The Americas | 12 Feb 1818[note 32] | 12 Feb 1818 | ||
| Asia | 1600 BC c. (Shang dynasty) [note 33] | 2 September 1945 | ||
| The Americas | 20 July 1810 | 7 Aug 1819 | ||
| Africa | 6 July 1975 | 6 July 1975 | ||
| Africa | 30 June 1960 | 30 June 1960 | ||
| Africa | 15 Aug 1960 | 15 Aug 1960 | ||
| Australia | 1965 | 4 August 1965 | ||
| The Americas | 14 Nov 1838 | 1838 | ||
| Europe | 8 Oct 1991[30][31][32][33][34] | 8 Oct 1991 | ||
| The Americas | 20 May 1902 | 2 February 1909 | ||
| Europe | 16 Aug 1960 | 16 Aug 1960 | ||
| Europe | 870 | 1 Jan 1993 | ||
| Europe | 714[35] | 5 May 1945 | ||
| Africa | 27 June 1977 | 27 June 1977 | ||
| The Americas | 3 Nov 1978 | 3 Nov 1978 | ||
| The Americas | 27 Feb 1844 [note 34] | 27 Feb 1844 | ||
| The Americas | 13 May 1830 | 13 May 1830 | ||
| Africa/Asia | 28 Feb 1922[note 35] | 28 Feb 1922 | ||
| The Americas | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 | ||
| Africa | 12 Oct 1968 | 12 Oct 1968 | ||
| Africa | 24 May 1993 | 24 May 1993 | ||
| Europe | 24 Feb 1918[36] | 20 Aug 1991 | ||
| Africa | 6 Sep 1968 | 6 Sep 1968 | ||
| Africa | 900 c. (Zagwe Kingdom)[note 36] | 5 May 1941 | ||
| Australia | 10 Oct 1970 | 10 Oct 1970 | ||
| Europe | 6 Dec 1917 | 4 Jan 1918 | ||
| Europe | 481 | 1944 | ||
| Africa | 17 Aug 1960 | 17 Aug 1960 | ||
| Africa | 18 Feb 1965 | 18 Feb 1965 | ||
| Asia/Europe | 26 May 1918 | 9 Apr 1991 | ||
| Europe | 1 July 1867 (North German Confederation) | 15 Mar 1991 | ||
| Europe | 25 Mar 1822 | 1945 | ||
| Africa | 6 May 1957 | 6 May 1957 | ||
| The Americas | 7 Feb 1974 | 7 Feb 1974 | ||
| The Americas | 17 Apr 1839 | 17 Apr 1839 | ||
| Africa | 2 Oct 1958 | 2 Oct 1958 | ||
| Africa | 24 Sep 1973 | 10 Sep 1974 | ||
| The Americas | 26 May 1966 | 26 May 1966 | ||
| The Americas | 1 Jan 1804 | 1 Jan 1804 | ||
| The Americas | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 | ||
| Europe | 895 | 1918
23 Oct 1989 |
||
| Europe | 1 Dec 1918 | 1 Dec 1918 | ||
| Asia | 15 Aug 1947 | 15 Aug 1947 | ||
| Asia/Australia | 17 Aug 1945 | 27 Dec 1949 | ||
| Asia | 1501 (Safavid Empire) [note 37] | 17 October 1941 | Anglo-Soviet withdrawal from Tehran | |
| Asia | 3 Oct 1932 | 1 May 2003 | ||
| Europe | 11 Dec 1931 [note 38] | 11 Dec 1931 | ||
| Asia | 14 May 1948 | 14 May 1948 | ||
| Europe | 1003 (County of Savoy) | 17 May 1861 | ||
| Africa | 7 Aug 1960 | 7 Aug 1960 | ||
| The Americas | 6 Aug 1962 | 6 Aug 1962 | ||
| Asia | 539 c. [note 39]. | 28 Apr 1952 | ||
| Asia | 25 May 1946 | 2 Aug 1958 | ||
| Asia/Europe | 16 Dec 1991 | 16 Dec 1991 | ||
| Africa | 12 Dec 1963 | 12 Dec 1963 | ||
| Australia | 12 July 1979 | 12 July 1979 | ||
| Asia | 9 Sep 1948 | 9 Sep 1948 | ||
| Asia | 15 Aug 1948 | 15 Aug 1948 | ||
| Asia | 1752 | Feb 1991 | ||
| Asia | 31 Aug 1991 | 31 Aug 1991 | ||
| Asia | 22 Oct 1953 | 22 Oct 1953 | ||
| Europe | 18 Nov 1918[37] | 4 May 1990 | ||
| Asia | 22 Nov 1943 | 31 Dec 1946 | ||
| Africa | 4 Oct 1966 | 4 Oct 1966 | ||
| Africa | 26 July 1847 | 26 July 1847 | American Colonization Society | |
| Africa | 24 Dec 1951[38] | 24 Dec 1951 | ||
| Europe | 16 Feb 1918 | 11 Mar 1990 | ||
| Europe | 15 Mar 1815 | 1945 | ||
| Africa | 26 June 1960 | 26 June 1960 | ||
| Africa | 6 July 1964 | 6 July 1964 | ||
| Asia | 31 Aug 1957[39] | 31 Aug 1957 | ||
| Asia | 26 July 1965 | 26 July 1965 | ||
| Africa | 20 Aug 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | ||
| Europe | 21 Sep 1964 | 21 Sep 1964 | ||
| Australia | 21 Oct 1986 | 21 Oct 1986 | ||
| Africa | 28 Nov 1960 | 28 Nov 1960 | ||
| Africa | 12 Mar 1968 | 12 Mar 1968 | ||
| The Americas | 16 Sep 1810 | 1864 | ||
| Australia | 3 Nov 1986 | 3 Nov 1986 | ||
| Europe | 27 Aug 1991 | 27 Aug 1991 | ||
| Europe | 2 Feb 1861 | 1945 | ||
| Asia | 29 Dec 1911 | 13 Mar 1921 | ||
| Europe | 21 May 2006[note 40] | 21 May 2006 (independence referendum)
June 3, 2006 |
||
| Africa | 788[40] | 7 Apr 1956 | ||
| Africa | 25 June 1975 | 25 June 1975 | ||
| Asia | 4 Jan 1948 | 4 Jan 1948 | ||
| Africa | 21 Mar 1990 | 21 Mar 1990 | ||
| Australia | 31 Jan 1968 | 31 Jan 1968 | ||
| Asia | 1559 c. (Gorkha Kingdom) | 1768 (Unification of Nepal) | (none) | |
| Europe | 26 July 1581 (de facto)
30 Jan 1648 (de jure) |
1945 | ||
| Australia | 25 Nov 1947 [note 41] | 25 Nov 1947 | ||
| The Americas | 29 Nov 1898 | 29 Nov 1898 | ||
| Africa | 3 Aug 1960 | 3 Aug 1960 | ||
| Africa | 1 Oct 1960 | 1 Oct 1960 | ||
| Europe | 8 Sep 1991 | 8 Sep 1991 | ||
| Europe | 872 | 8 May 1945 | ||
| Asia | 1626 [note 42] | 1743 | ||
| Asia | 14 Dec 1947 | 14 Dec 1947 | ||
| Australia | 1 Oct 1994 | 1 Oct 1994 | ||
| Asia | Sovereignty disputed by |
15 Nov 1988 | ||
| The Americas | 3 Nov 1903 | 31 Jan 1990 | ||
| Australia | 16 Sep 1975 | 16 Sep 1975 | ||
| The Americas | 14 May 1811 (de facto)
Nov 25, 1845 (formal declaration of Independence) |
1876 | ||
| The Americas | 28 July 1821 | 25 Aug 1839 | ||
| Asia | 4 July 1946 [note 43] | 4 July 1946 [note 44] | ||
| Europe | 11 November 1918 (as a new state, not as a nation) | 1945 | ||
| Europe | 25 July 1139 | 30 Aug 1808 | ||
| Asia | 3 Sep 1971 | 3 Sep 1971 | ||
| Europe | 13 July 1878 | 13 July 1878 | ||
| Asia/Europe | 1471 (Grand Duchy of Moscow) | 26 Dec 1991 (de facto) | ||
| Africa | 1 July 1962 | 1 July 1962 | ||
| The Americas | 19 Sep 1983 | 19 Sep 1983 | ||
| The Americas | 22 Feb 1979 | 22 Feb 1979 | ||
| The Americas | 27 Oct 1979 | 27 Oct 1979 | ||
| Australia | 1 Jan 1962 | 1 Jan 1962 | ||
| Europe | 1243 | 21 Sep 1944 | World War II Allies | |
| Africa | 12 July 1975 | 12 July 1975 | ||
| Asia | 13 Jan 1902 (Emirate of Riyadh)[note 46] | 23 Sep 1932 | ||
| Africa | 20 Aug 1960 | 20 Aug 1960 | ||
| Europe | 13 July 1878 (as a new state, not as a nation.) [note 47] | 3 June 2006 | ||
| Africa | 29 June 1976 | 29 June 1976 | ||
| Africa | 27 Apr 1961 | 27 Apr 1961 | ||
| Asia | 9 Aug 1965 | 9 Aug 1965 | ||
| Europe | 1 Jan 1993 | 1 Jan 1993 | ||
| Europe | 25 June 1991 | 25 June 1991 | ||
| Australia | 7 July 1978 | 7 July 1978 | ||
| Africa | 1 July 1960 | 1 July 1960 | ||
| Africa | 11 Dec 1931[note 48] | 11 Dec 1931 | ||
| Africa | 9 July 2011 | 9 July 2011 | ||
| Europe | 542 (Visigothic Spain of Toledo) [note 49][42] | 1813 | ||
| Asia | 4 Feb 1948 | 4 Feb 1948 | ||
| Africa | 1 Jan 1956 [note 50] | 1 Jan 1956 | ||
| The Americas | 25 Nov 1975 | 25 Nov 1975 | ||
| Europe | 970c. | 970 | none | |
| Europe | 24 Oct 1648 | 1815 | ||
| Asia | April 17, 1946 | 28 Sep 1961[note 51] | ||
| Asia | 9 Sep 1991 | 9 Sep 1991 | ||
| Africa | 9 Dec 1961 | 9 Dec 1961 | ||
| Asia | 4 Mar 1351 (Ayutthaya Kingdom) | 1945 | ||
| Asia | 28 Nov 1975 | 20 May 2002 | ||
| Africa | 27 Apr 1960 | 27 Apr 1960 | ||
| Australia | 4 June 1970 | 4 June 1970 | ||
| The Americas | 31 Aug 1962 | 31 Aug 1962 | ||
| Africa | 20 Mar 1956 | 20 Mar 1956 | ||
| Asia/Europe | 1299[note 52] | 1923 | ||
| Asia | 27 Oct 1991 | 27 Oct 1991 | ||
| Australia | 1 Oct 1978 | 1 Oct 1978 | ||
| Africa | 9 Oct 1962 | 9 Oct 1962 | ||
| Europe | 24 August 1991[note 53] | 24 Aug 1991 | ||
| Asia | 2 Dec 1971 | 2 Dec 1971 | ||
| Europe | 498 (Dál Riata) [note 54] | 1266 | ||
| The Americas | 4 July 1776 | 19 Oct 1781 | ||
| The Americas | 25 Aug 1825 | 27 Aug 1828 | ||
| Asia | 1 Sep 1991 | 1 Sep 1991 | ||
| Australia | 30 July 1980 | 30 July 1980 | ||
| Europe | 11 Feb 1929 | 11 Feb 1929 | ||
| The Americas | 13 Jan 1830 | 13 Jan 1830 | ||
| Asia | 2 Sep 1945 | 2 July 1976 | ||
| Asia | 1 Nov 1918 | 22 May 1990 | ||
| Africa | 24 Oct 1964 | 24 Oct 1964 | ||
| Africa | 11 Nov 1965 | 18 Apr 1980 |
Yugoslavia Legacy[edit]
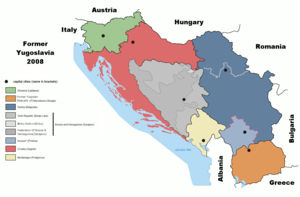
The present-day states which succeeded Yugoslavia are still today sometimes collectively referred to as the former Yugoslavia (or shortened as Ex-Yu or similar). These countries are, listed chronologically:
- Croatia (since 25 June 1991)
- Slovenia (since 25 June 1991)
- North Macedonia (since 25 September 1991; formerly Macedonia)
- Bosnia and Herzegovina (since 3 March 1992)
- Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro; 1992–2006)
- Montenegro (since 3 June 2006)
- Serbia (since 5 June 2006)
- Kosovo (since 17 February 2008; independence disputed)
Before 19th century[edit]
| Year | Previous entity | Newly independent entity | Event |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1480 | Great Horde | Grand Duchy of Moscow | |
| 1581 | Spain | Dutch Republic | |
| 1640 | Iberian Union | Portugal | |
| 1776 | Great Britain | United States |
19th century to World War I[edit]
Interwar period[edit]
Cold War[edit]
Post–Cold War era[edit]
| Year | Previous entity | Newly independent entity |
|---|---|---|
| 1992 | Yugoslavia | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Federal Republic of Yugoslavia |
| 1993 | Federation of Ethiopia and Eritrea (Ethiopia) | Eritrea |
| 1994 | Palau | |
| Palestinian National Authority (self-declared State of Palestine) | ||
| 2002 |
|
East Timor |
| 2006 | Serbia, Montenegro | |
| 2008 |
|
Kosovo |
| 2011 | Sudan | South Sudan |
| 2014 | Ukraine | Donetsk People's Republic, Luhansk People's Republic |
See also[edit]
- Age of Revolution
- Decolonization
- Human history
- List of national independence days
- List of sovereign states by date of formation
- List of wars of independence
- Modern era
- Timeline of national flags
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b c d Cite error: The named reference
SFRJwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b c The annexation of the Baltic states in 1940 is considered an illegal occupation by the current governments of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania and by a number of Western countries, including the United States and the European Union, who assert that the states were independent countries occupied by the Soviet Union. The three corresponding Soviet republics were officially sovereign entities in a federation, according to Article 76 of the Constitution of the Soviet Union. However, the Soviet Union was heavily centralized and was de facto a single federal state and the three states consider the corresponding Soviet republics to have been illegitimate entities.
- ^ After independence the United States colonized and later incorporated in their federal structure, territories on their own. The last acquisition in the Americas was in 1935, the last incorporation in 1959, but some of the territories remain unincorporated.
- ^ Not recognized by France until April 17, 1825.
- ^ Not recognized by Spain until April 29, 1857.
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. The date September 18, 1810 (when the Government Junta was formed) is celebrated as Chile's date of independence. Chile would not be recognized by Spain until April 25, 1844.
- ^ Celebrated as Battle of Boyacá Day. The date July 20, 1810 (when Viceroy Antonio José Amar y Borbón formally declared New Granada's independence) is celebrated as Colombia's date of independence.
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. After declaring independence from Spain on July 5, 1811 with the enactment of the Venezuelan Declaration of Independence, the territory of present-day Venezuela continued to struggle for its independence until June 24, 1821 when the decisive victory of Simón Bolívar and Venezuelan forces over the Spanish at the Battle of Carabobo led to the independence of the country from Spain and the establishment of the Republic of Gran Colombia, from which Venezuela gained independence on January 13, 1830. Venezuela celebrates July 5, 1811 as its independence day.
- ^ a b c d e After gaining independence from Spain, the Federal Republic of Central America was annexed by the Mexican Empire on January 25, 1822. The Federal Republic would regain independence on July 1, 1823.
- ^ On November 15, 1838, Costa Rica formally withdrew from the Federal Republic of Central America and then declared itself as an independent republic on September 28, 1848
- ^ Sometime around 1840 Guatemala formally withdrew from the Federal Republic of Central America and became an independent republic on March 21, 1847.
- ^ On November 15, 1838, Honduras formally withdrew from the Federal Republic of Central America and became an independent state.
- ^ On February 18, 1841, El Salvador (by then the only member remaining in the Federal Republic of Central America), formally withdrew and became an independent state.
- ^ as the Republic of Spanish Haiti
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. After gaining independence from Spain, the Republic of Spanish Haiti was annexed by Haiti on February 9, 1822. On November 6, 1844, after months of fighting starting from February 27 of that year, the Dominican Republic regained sovereignty upon the ratification of the Constitution of the Dominican Republic. The February 27 date is celebrated as the Dominican Republic's date of independence.
- ^ Celebrated as Battle of Pichincha Day. The date August 10, 1909 (when the city of Quito formally declared Ecuador's independence) is celebrated as Ecuador's date of independence. On May 13, 1830, Ecuador formally seceded from Gran Colombia.
- ^ Not recognized by Spain until July 21, 1847.
- ^ As the Empire of Brazil.
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. Brazil’s independence from Portugal was officially recognized on August 29, 1825 by the Treaty of Rio de Janeiro. The date September 7, 1822 (when then-Prince Regent Dom Pedro formally declared Brazil's independence) is celebrated as Brazil's date of independence.
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. After its decisive victory over Spanish forces at the Battle of Las Piedras, Uruguay continued to struggle for its independence against Spain. From 1816 to 1820, the territory of present-day Uruguay was invaded and conquered by the Portuguese Empire during the Portuguese conquest of the Banda Oriental. Uruguay was formally annexed firstly by the Portuguese Empire in 1821 and secondly by the Empire of Brazil in 1822 as a Brazilian province under the name Cisplatina. Uruguay declared independence from the Empire of Brazil on August 25, 1825, but its independence was officially recognized on August 27, 1828 by the Preliminary Peace Convention. Uruguay celebrates August 25, 1825 as its independence day.
- ^ On March 18, 1861, the Dominican Republic under Pedro Santana formally rejoined the Spanish Empire as a colony. This proved to be very unpopular among the Dominican people, and on August 16, 1865, the Dominican Republic became independent once again.
- ^ Celebrated as Restoration Day.
- ^ Celebrated as Canada Day. The Dominion of Canada was constituted through the Constitution Act, 1867 entering into force on July 1, 1867. On December 11, 1931, it got increased self-governance powers through the Statute of Westminster, followed by complete sovereignty on April 17, 1982, after the passage of the Canada Act 1982. Because of these decades-long steps, Canada Day is not considered to be a celebration of Canada's independence (although it is usually celebrated as such).
- ^ De jure. De facto the
 United States.
United States.
- ^ Date marking the end of Spanish rule over Cuba. Not celebrated as a holiday. From this date to May 20, 1902, Cuba was occupied by the United States, supposedly to help Cuba prepare for independence. However, the terms of the Platt Amendment meant that the United States continued to dominate Cuba long after independence, including another period of occupation. This dominance would last until the end of the Cuban Revolution on January 1, 1959. As a result, Cuba celebrates the date October 10, 1868, as its date of independence, when Carlos Manuel de Céspedes formally declared Cuba's independence and launched the Ten Years' War.
- ^ Abolished its commonwealth monarchy on August 1, 1976.
- ^ Abolished its commonwealth monarchy on February 23, 1970.
- ^ Full sovereignty. Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ Austrians date their national identity back to the establishment of the Duchy of Austria (later the Archduchy of Austria) in the Middle Ages (a state of the Holy Roman Empire that only had full sovereignty after the dissolution of the Empire in the 19th century). Another important states in the identity of the Austrian nation is the Austrian Empire, Cisleithania, Republic of German-Austria, the First Austrian Republic, Federal State of Austria (this later annexed by Nazi Germany). As an independent and sovereign state the current Austrian state dates back to 1945, when the country seceded from Nazi Germany after the end of World War II. However the Moscow Conference of 1943 declared the German annexation of Austria in 1938 null and void
- ^ The medieval Principality of Polotsk became an extinct state after its dissolution. Modern state of Belarus dates from 1991
- ^ Full sovereignty. Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Canada becomes completely sovereign, having consulates and embassies in other countries
- ^ The Kingdom of Chile (Patria Vieja) became an extinct state after its reconquest by Spain. Modern state of Chile dates from 1818
- ^ People's Republic of China consider itself the successor state of the Republic of China, the latter considers itself the successor state of the Qing Empire, and through the mandate of heaven all Chinese imperial states considered themselves successors to previous dynasties, with the Shang dynasty being historically the first non-legendary dynasty of that country.
- ^ The Republic of Spanish Haiti became an extinct state after its reconquest by Haiti. Modern state of Dominican Republic dates from 1844
- ^ Egypt is one of the oldest nations in the world, its national identity dating back to the First Dynasty of Ancient Egypt. But it is important to stress the difference between state and nation. As a state the nation lost its sovereignty and was conquered by other states several times in History. The current Egyptian state, as an independent sovereign state, dates from 1922
- ^ Zagwe was one of the kingdoms that emerged from the collapse of the Kingdom of Aksum, that became an extinct or abolished state in 960 AD. It is the direct historical predecessor of the Ethiopian Empire, regardless of the Solomonic dynasty of the ancient Kingdom of Aksum having overthrown the Zagwe dynasty in 1270 and assumed their throne. Dynastic lineages are irrelevant to current international law, mainly because of the fact of the majority of the states in the current world scenario are republics.
- ^ Iran is one of the oldest nations in the world, its national identity dating back to the Median Empire and the Achaemenid Empire. But it is important to stress the difference between state and nation. As a state the nation lost its sovereignty and was conquered by other states several times in History. The current Iranian state, as an independent state in a contiguous way, dates from 1501
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931. Internationally recognized independence, by nations that aren't members of the Commonwealth of Nations
- ^ Beginning of the reign of the first Japanese emperor proven to have existed historically
- ^ Montenegrins date their national identity to the founding of Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro in 1516. However, the Montenegrin state became an extinct state at the time of the Podgorica Assembly, which led to the annexation and extinction of the Kingdom of Montenegro by the Kingdom of Serbia. The current Montenegrin state emerged in 2006 after separating from Serbia.
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ The region was conquered by Portuguese forces under the command of Afonso de Albuquerque in 1507, and remained under Portuguese control until they were expelled by the Ya'rubids.
- ^ The First Philippine Republic was an unrecognized state and became an extinct state after being terminated by the United States. Modern state of Philippines dates from 1946. However, Filipinos celebrate their independence date on June 12 (the date of establishment of the First Philippine Republic) in order to avoid celebrating their national date on the same day that their former colonizers (the USA) celebrate their national date (July 4).
- ^ Independence recognized via the Treaty of Manila (1946).
- ^ Russia dates its national identity back to the Kievan Rus, medieval state that was extinguished when it was conquered by the Mongols of the Golden Horde. A new Russian state arose and existed continuously and without loss of sovereignty from 1480 until 1922, when of its own accord it ceased to be a sovereign state and became a subnational unit of the Soviet Union. With the dissolution of the Soviet Union, the nation again had a sovereign state, with the current Russian sovereign state dating back to 1991. The Russian Federation is regarded as the successor state to the former Soviet Union, inheriting its seat as a UN member state, after a letter by president Boris Yeltsin was received by the secretary-general Javier Pérez de Cuéllar.
- ^ Saudi Arabia dates its national identity from the establishment of the Emirate of Diriya (First Saudi State), however this state later became extinct, as did the Emirate of Nejd (the Second Saudi State). The current and Third Saudi State came into being in 1903 when it separated from the Emirate of Jabal Shammar. Through wars of conquest it conquered other states and made a real union with Hejaz before adopting the current name Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932
- ^ Serbia consider itself as the successor state of Yugoslavia. The current Serbian state emerged in 1878, after independence de jure from the Ottoman Empire. Other Serbian states existed before this date, but ceased to exist due to the conquest of other states. It is important not to confuse the concept of state with that of the nation, as a nation the Serbian people have existed since the Middle Ages, and just like other ethnic groups (such as the Greeks, Jews, Egyptians, etc.) it went through periods of its history in which it was a Stateless nation
- ^ Adoption of the Statute of Westminster 1931
- ^ During the Visigoth kingdom of Toledo, the names of the Visigoth kingdom (Regnum Gothorum) and Spain (Hispaniae or Spaniae) were used more and more frequently as synonymous terms, beginning to have not only a geographical meaning, but also a political one (especially since the year 624, when Swinthila finally defeated the Byzantines and the Visigoths dominated the entire Iberian Peninsula). Historiographers of the time such as Isidore of Seville, Julian of Toledo, John of Biclaro, as well as from abroad, the Franks Gregory of Tours, Fredegar, or Pope Leo II, referred to the Visigoth kingdom or its kings, as Hispania or kings of Hispania. On the other hand, there was an adoption by the Visigoths of the Hispano-Roman culture, with a progressive intention to merge the Gothic and Hispano-Roman societies into a common one, politically (kingdom administered from the capital of Toledo, and in accordance with Roman ecclesiastical power through the Councils of Toledo), religiously (Reccared I converted from Arianism to Chalcedonian Christianity in 589), common legislation (Code of Leovigild, and later Visigothic Code), militarily (army composed of Hispano-Romans and Visigoths), with a monetary unit (Visigothic royal currency from 580 to 710), and linguistically (Visigoths spoke Latin), taking advantage of the pre-existing cohesion left by the Hispania of the Roman Empire.[41] Spain is a unitary state that emerged from the political union by incorporating union of different states throughout history. Using the modern criteria of the United Nations, which considers the date of admission of other states that emerged from political unions (such as Tanzania, Malaysia and Yemen) as the date of the oldest predecessor state to be admitted, it will soon be seen that the oldest state that merged to form modern Spain is the Kingdom of León, one of the states in personal union that integrated the Crown of Castile, with such state dating its origins directly from the Kingdom of Asturias. Spain was until 1715 a composite monarchy, i.e. several small states in personal union, only passing through a political union in 1715 with the Nueva Planta decrees
- ^ Sudan dates its national identity to the Kingdom of Kerma, Kingdom of Kush and other ancient kingdoms that existed in its territory, i.e Nubia (mentioned in ancient Egyptian texts). However, as an independent sovereign state, the current Sudanese state dates back to 1956.
- ^ By uniting with Egypt to form the United Arab Republic into a political union, the Second Syrian Republic ceased to exist as a sovereign state and became an extinct state, with Syria becoming a subnational unit of the United Arab Republic. The current Syrian state emerged as a new state when it broke up politically in 1961. However, Syrians celebrate April 17 as their independence day, as it was on April 17, 1946 that the nation ceased to be a colony of France.
- ^ The Republic of Turkey is the successor state of the Ottoman Empire. Despite being known in English as the Turkish War of Independence, Turks call it in their language Kurtuluş Savaşı (lit. Liberation War). "War of Independence" in Turkish is "bağımsızlık savaşı". The country's national date is the Republic Day (Cumhuriyet Bayramı), which commemorates the change of government regime from a monarchy to a republic.
- ^ Ukraine dates its national identity back to the Kievan Rus, however this state became an extinct state when it was conquered by the Mongols of the Golden Horde. Another state with historical importance for Ukrainians in their national identity is the medieval Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, which however also became an extinct state. In the 17th century the Ukrainian nation established another Ukrainian state, the Cossack Hetmanate, however this state became extinct upon being conquered by the Russian Empire. Between 1917 and 1919, two new Ukrainian states was established, being unified in 1919 but again lost its sovereignty by becoming a subnational unit of the Soviet Union. The current Ukrainian sovereign state dates from 1991, emerging after the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
- ^ The United Kingdom is a unitary state that emerged from the political union by incorporating union of different states throughout history. Northern Ireland has been part of this political union since 1922, when the rest of Ireland separated from the United Kingdom. Ireland had united with Great Britain in 1800 to form the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The Kingdom of Great Britain itself emerged from the political union between the Kingdom of England (which had already conquered and annexed the Principality of Wales centuries before) and the Kingdom of Scotland. Using the modern criteria of the United Nations, which considers the date of admission of other states that emerged from political unions (such as Tanzania, Malaysia and Yemen) as the date of the oldest predecessor state to be admitted, it will soon be seen that of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom (today subnational units and not sovereign countries) the oldest is Scotland (unified in 843), which dates its origin to the Dál Riata, which conquered the existing small Pictish states in future Scotland to form the Kingdom of Scotland, which existed until 1707 when it merged with England (originated in 927, when the various Anglo-Saxon kings swore their allegiance to Æthelstan of Wessex (r. 924–939), unifying most of modern England under a single king
References[edit]
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
SovietSovereignRepublicwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Transcontinental country, partially located in Asia.
- ^ Not celebrated as a holiday. Netherlands New Guinea was separated from the Dutch East Indies on 29 December 1949. Following skirmishes with Indonesia in 1961 and the New York Agreement, the Netherlands transferred the authority of Dutch New Guinea to a UN protectorate on 1 October 1962 and it was integrated into Indonesia on 1 May 1963. The date 17 August 1945 (when Sukarno formally proclaimed Indonesia's independence) is celebrated as Indonesia's date of independence.
- ^ As a League of Nations mandate and later UN Trust Territory Nauru was under effective Australian administration with the United Kingdom and New Zealand as nominal co-trustees.
- ^ As the Dominion of Fiji.
- ^ Celebrated as Fiji Day. (While Fiji does not have a holiday called Independence Day, Fiji Day is celebrated as such). On 7 October 1987 after two military coups, Fiji formally abolished its Commonwealth monarchy and became a republic.
- ^ The main part of German New Guinea after the World War I became a League of Nations mandate and later a UN Trust Territory as the Territory of New Guinea under Australian administration. The Territory of Papua was a British colony transferred to the British Dominion of Australian administration in 1902.
- ^ Vanuatu was a joint British-French Condominium
- ^ King, Joan Wucher (1989) [First published 1984]. Historical Dictionary of Egypt. Books of Lasting Value. American University in Cairo Press. pp. 259–260. ISBN 978-977-424-213-7.
- ^ "The World Factbook: Field Listing: Independence". Archived from the original on 2013-02-27. Retrieved 2018-05-12.
- ^ "National Day 2022, 2023 and 2024 in Bahrain". Archived from the original on 21 October 2023. Retrieved 12 May 2018.
- ^ An Outline of the People's Republic of Albania. 8 Nëntori. 1978. p. 47.
- ^ The Regency of Algiers ceased to exist and became an extinct or abolished state when France conquered Algeria. The People's Democratic Republic of Algeria is a new state that emerged after separating from the French Republic
- ^ Shillington, Kevin (2005). Encyclopedia of African history. CRC Press. p. 60. ISBN 1-57958-453-5.
- ^ Blaustein, Albert P.; Sigler, Jay A.; Beede, Benjamin R. (1977). Independence documents of the world. Brill Archive. p. 11. ISBN 0-379-00794-0.
- ^ Whittlesey, Derwent (June 1934). "Andorra's Autonomy". The Journal of Modern History. 6 (2): 147–155. doi:10.1086/236113. S2CID 145133794.
- ^ Archambault, G.H. (Nov 16, 1944). "Andorra Occupied by French Police; De Gaulle Acts Under Historic Authority to Keep Order in Pyrenees Republic". The New York Times. p. 5. Retrieved April 25, 2009.
- ^ "1975: Divided Angola gets independence". BBC On This Day. 1975-11-11. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Background Note: Antigua and Barbuda". state.gov. US Department of State. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ "Congress of Tucumán". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Howe, G. Melvyn; Dowsett, Charles James Frank; Mints, Aleksey Aleksandrovich; Suny, Ronald Grigor (23 April 2019). "Armenia: Independence". Britannica.com.
- ^ Kurian, George Thomas (1987). The Encyclopedia of the Third World. Vol. 1 (3rd ed.). Facts on File. p. 115. ISBN 0-8160-1118-4.
- ^ "U.S. Relations With Belize". state.gov. US Department of State. December 22, 2016.
- ^ "Botswana". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ "Brazil". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ "Bulgaria". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ "Burkina Faso". Encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2009-07-18.
- ^ Tucker, Spencer (1999). Vietnam. Routledge. pp. 196–197. ISBN 1-85728-922-6.
- ^ "Background Note: Cape Verde". state.gov. US Department of State. June 2008. Retrieved 26 July 2009.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Hrvatska povijestwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Grboslovlje u Hrvata Krunisaniwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
geni.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
visitecroatia.comwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Croatia – World Leaders Indexwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ McKitterick, Rosamond, ed. (1995). The New Cambridge Medieval History. Volume II c.700–c.900. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 205. ISBN 0-521-36292 X.
- ^ "Estonian Declaration of Independence, 24 February 1918". President of the Republic of Estonia. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ "November 18, 1918 – Proclamation of Latvia's independence". LETA. Archived from the original on 29 October 2008. Retrieved 2009-07-19.
- ^ At the end of World War II, the region was abandoned by the Italians. The French and British occupy the region militarily, with the French settling in Fezzan, the British in Tripolitania and the Emirate of Cyrenaica being established as an independent country. King Idris I unified the country on December 24, 1951, uniting the territories into a single federal state, named the United Kingdom of Libya, later becoming the unitary Kingdom of Libya
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Federation of Malaya Independence Actwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ The independent government of the Moroccan Sultan still existed, in nominal form, during the period when the country was a protectorate of European colonial powers. Source: Treaty of Fes
- ^ "El concepto de España en la historiografía visigoda y asturiana" (The concept of Spain in Visigothic and Asturian historiography). Alexander Pierre Bronisch, 2006.
- ^ Hispania-Spania. El nacimiento de España. Conciencia hispana en el reino visigodo de Toledo (Santiago Cantera Montenegro). Hispania-Spania. The birth of Spain. Hispanic consciousness in the Visigothic Kingdom of Toledo. (Santiago Cantera Montenegro)
- ^ a b The Japanese rule over French Indochina is usually seen on par with other occupations at that time.
- ^ The Italian rule over Ethiopia is often put on par with other occupations at that time despite its administration showing characteristics of colonial rule. Probably motivated by its short duration spanning only 5 years.
- ^ Occupied by Germany.
- ^ a b c The date of formation of the current states of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania is subject to an international dispute. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania all maintain that they were illegally occupied by the Soviet Union, and that the current states are direct continuations of the pre-WWII states, which continued to exist through governments-in-exile. Russia maintains that the current three states are legally distinct entities newly created after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. All three states were admitted the UN as independent nations, not successor states of the USSR. For more information, see State continuity of the Baltic states.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).
