User:Mr. Ibrahem/Rifaximin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xifaxan, Xifaxanta, Normix, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a604027 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | < 0.4% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 6 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (97%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
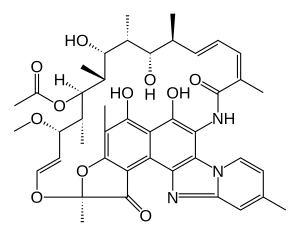
| Formula | C43H51N3O11 |
| Molar mass | 785.891 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Rifaximin, sold under the trade name Xifaxan among others, is an antibiotic used to treat hepatic encephalopathy, irritable bowel syndrome, and traveler's diarrhea.[1] Specifically it can be used to decrease the number of episodes of hepatic encephalopathy.[2] It is not effective for a number of types of diarrhea including Salmonella.[1] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include nausea, headache, and abdominal discomfort.[1] Other side effects may include joint pain, mood changes, swelling, skin rash, and Clostridium difficile colitis.[2][1] Use in pregnancy is not recommended while use during breastfeeding is believed to be safe for the baby.[2] It is in the rifamycin family of medications.[2]
Rifaximin was approved for medical use in the United States in 2004.[1] In United States the dose for hepatic encephalopathy costs $1,864 per month as of January 2017.[3] In the UK, 56 tablets of the 550mg dose costs the NHS around 260 pounds as of 2020.[2] As of 2020 no generic version is available in the United States.[4]
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g "Rifaximin". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f BNF (80 ed.). London: BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 609. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ "NADAC as of 2017-01-25". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 2017-02-02. Retrieved 25 January 2017.
- ^ "Generic Xifaxan Availability". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 5 June 2016. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
