Divyamani
| Arohanam | S R₁ G₂ M₂ P D₃ N₃ Ṡ |
|---|---|
| Avarohanam | Ṡ N₃ D₃ P M₂ G₂ R₁ S |
| Carnatic music |
|---|
 |
| Concepts |
| Compositions |
| Instruments |
|
Divyamani (pronounced Divyamaṇi,[1] meaning the divine gem) is a rāgam in the 72 melakarta rāgam system of Carnatic music. It is the 48th in the series. It is called Jeevantika[1] or Jeevantini[2][3] in Muthuswami Dikshitar school of Carnatic music.
Structure and Lakshana[edit]
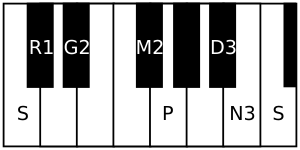
It is the 6th rāgam in the 8th chakra Vasu. The mnemonic name is Vasu-Sha. The mnemonic phrase is sa ra gi mi pa dhu nu.[2] Its ārohaṇa-avarohaṇa structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see swaras in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms):
(the notes used in this scale are shuddha rishabham, sadharana gandharam, prati madhyamam, shatsruthi dhaivatham, kakali nishadham)
As it is a melakarta rāgam, by definition it is a sampoorna rāgam (has all seven notes in ascending and descending scale). It is the prati madhyamam equivalent of Roopavati, which is the 12th melakarta.
Janya rāgams[edit]
Divyamani has a few minor janya rāgams (derived scales) associated with it. See List of janya rāgams for all rāgams associated with Divyamani.
Compositions[edit]
A few compositions set to Divyamani are:
- Leela ganu joochi by Thyagaraja
- Appa muruga by Koteeswara Iyer
Related rāgams[edit]
This section covers the theoretical and scientific aspect of this rāgam.
Divyamani's notes when shifted using Graha bhedam, yields no other melakarta rāgam.
